TANISAWA, Kumpei
Doctoral Program / SPORTS MEDICINE SPECIALIZATION / Sports Biochemistry and Genetics
- SUBJECTS
- Genome, genetic variation, gut microbiome, physical activity, nutrition, health
- PROFILE
- Dr. Kumpei Tanisawa is Assistant Professor at Faculty of Sport Sciences, Waseda University, Japan. His research area of interest is exercise biochemistry and sport genomics. He is mainly performing human studies to identify genomic and molecular markers that predict the inter-individual variability in response to exercise and nutrition in terms of health and athletic performance. To achieve this goal, he mainly uses a comprehensive approach by utilizing omics data (e.g., genome, transcriptome, and microbiome) generated by next generation sequencer or microarray. Another his project is the whole genome sequencing of Kenyan and Ethiopian runners to understand the genetic architecture of their extreme endurance performance.
- BIOGRAPHY
- 2006–2010: School of Sport Sciences, Waseda University
2010–2012: Graduate School of Sport Sciences (Master's Program), Waseda University
2012–2015: Graduate School of Sport Sciences (Doctoral Program), Waseda University
2014–2015: Research Fellow of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (DC2)
2015–2019: Research Fellow of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (PD)
2016–2019: Research Fellow, National Institute of Biomedical Innovation, Health and Nutrition
2018–2019: Visiting Researcher, University of Brighton
2019–2022: Assistant Professor, Faculty of Sport Sciences, Waseda University
2022– : Associate Professor, Faculty of Sport Sciences, Waseda University
Degree: Ph.D. (Sport Sciences)
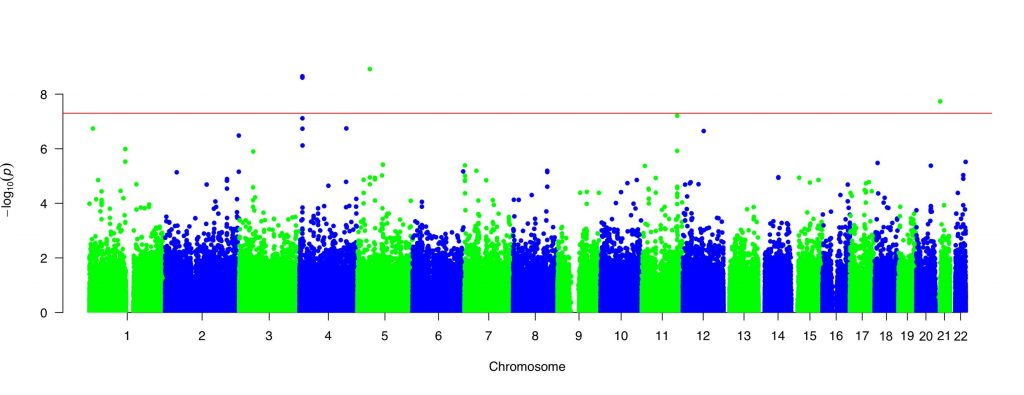
This figure is a Manhattan plot showing results of a genome-wide association study (GWAS). GWAS is a comprehensive approach that analyzes a large number of genetic variants across the entire genome to explore the association between these variants and traits. The horizontal axis indicates the chromosomal position of each variant analyzed in GWAS, whereas the vertical axis indicates the minus log transformed p-values obtained from the association analysis of each variant with a target trait. Each dot represents the strength of the evidence against the null hypothesis, and the dots in the upper side represent a strong evidence. Dr. Tanisawa is performing GWASs to identify the genetic variants associated with exercise-related traits (e.g., cardiorespiratory fitness, skeletal muscle mass, circulating myokine levels).
- MEMBERS
- ADMISSIONSIf you are interested in our school,
please see this page for admission information.